Key takeaways
Many seniors can still get erections, but ED becomes more likely with age and health issues.
Drugs like Cialis and Viagra can work well, but the best option depends on lifestyle, preferences, and health. Healthcare providers usually start seniors on lower ED drug doses to reduce side effect risks.
Always discuss ED drugs with your provider to pick the safest option for your health needs.
Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
Key takeaways
Many seniors can still get erections, but ED becomes more likely with age and health issues.
Drugs like Cialis and Viagra can work well, but the best option depends on lifestyle, preferences, and health. Healthcare providers usually start seniors on lower ED drug doses to reduce side effect risks.
Always discuss ED drugs with your provider to pick the safest option for your health needs.
Note to readers: While this article uses gendered terms like “man,” it’s referring to individuals with a penis. Ro understands that not everybody who identifies as a man has the same anatomy.
Can a 70-year-old man still get hard? The TLDR is yes, they can. While it may be more difficult to achieve and maintain an erection as a man ages, it doesn’t mean senior-aged men have to suffer from sexual dysfunction.
The best ED drug for seniors varies, depending on the individual. Medications like tadalafil (Cialis) and sildenafil (Viagra) are often prescribed and effective. The right choice depends on your needs, preferences, and health. Talk to your healthcare provider to find the best solution.
In this article, we’ll explore options for the best erectile dysfunction (ED) drugs for seniors and how to enjoy a vibrant sex life well into your 60s and above.
What is the best ED drug for seniors?
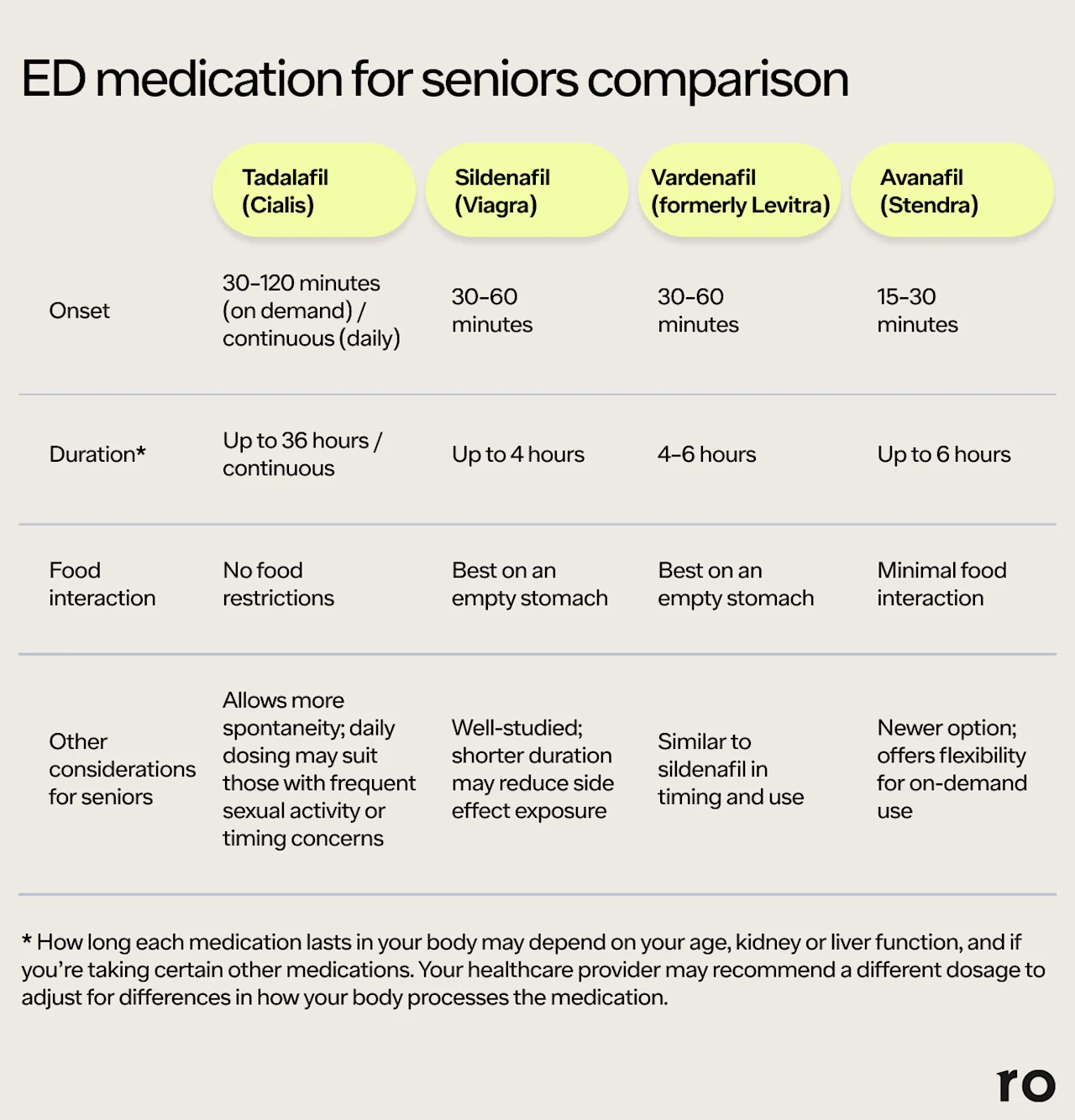
There’s no specific “best” ED drug for seniors, as it’s different for everyone. The right choice depends on your individual health profile, other medications, and personal preferences.
For example, tadalafil is well-tolerated, with effects lasting up to 36 hours, which gives you more flexibility with timing. This longer window can reduce performance anxiety and eliminate the need to plan sexual activity around taking your medication. And unlike other ED medications, tadalafil isn’t affected by food.
Sildenafil is a well-studied medication for ED that lasts up to four hours. This shorter duration may reduce exposure to side effects for some people.
Vardenafil and avanafil are two other commonly prescribed ED drugs that can kick in within 30 minutes and last up to six hours.
Another option, great for those who prefer not to take a pill, is Daily Rise Gummies. It contains 7 mg of tadalafil in a convenient gummy form, starting at $69 per month. Though this particular formulation is not US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved, it is composed of active ingredients that have been FDA-approved for ED.
How effective are ED medications for seniors?
The effectiveness of ED medications for seniors varies by person. The answer isn’t definitive and depends on careful medical evaluation and overall health.
Don't give up if your first ED medication doesn't work. If you've tried oral medications before without success, you might respond much better to a different option. And remember, ED medications don’t cause erections on their own; sexual stimulation is still needed for them to work.
Research shows that while sildenafil and tadalafil work equally well with similar side effects, tadalafil helps people feel more confident with their ED treatment, which can really matter when you're dealing with performance anxiety.
Sildenafil usually lasts around four hours, while tadalafil can remain effective for up to 36 hours. Both typically take 30 to 60 minutes to kick in, but factors like general health can affect timing.
People with severe ED can often benefit from combining treatments. Some healthcare providers prescribe daily tadalafil alongside on-demand sildenafil to boost erectile function, especially when dealing with more stubborn cases.
Your provider will help you find the right medication for your situation. They'll consider your other medications, heart health, and kidney function to determine which ED drug will work safest and most effectively for you.
How can men get hard after 60?
“How to get a hard-on at 60” is a common question. Studies found that those in their 60s are over 20 times more likely to be diagnosed or treated for ED compared to those in their 20s, which highlights just how common ED becomes with age.
Men over 60 looking for ED cures for seniors can still achieve erections through medical treatments. The same ED medications that work for younger men, including sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (formerly Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra), are effective for those in their 60s.
However, your healthcare provider may recommend starting with lower doses and monitoring for interactions with other medications you might be taking for conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes.
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and not smoking can significantly improve erectile function at this age.
How can men get hard after 70?
A 70-year-old man can still get hard, though ED is more common with age. Many older men retain sexual function, but health issues or lifestyle may cause problems. Treatments like medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes can help. Talk with a healthcare provider for personalized care.
Men over 70 face higher rates of ED, with studies showing that up to 80-90 % of men in their early 70s report some ED, and prevalence continues to rise with advancing age, though not every man is affected.
The same PDE5 inhibitor medications continue to work for those in their 70s, though healthcare providers typically use more caution because of the increased likelihood of heart conditions, diabetes, and other health issues that can affect both erectile function and medication safety.
At this age, addressing underlying health conditions becomes even more critical, as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression can significantly impact erectile function.
Your healthcare provider may need to adjust dosages or consider alternative treatments based on your overall health profile and the medications you’re already taking.
How can men get hard after 90?
There’s no specific age when a man stops getting erections. While ED becomes more common with age, many men, even into their 90s, can still get and maintain erections with the right support.
Research suggests that about 40% of men experience some form of ED by their 40s, and that number increases by roughly 10% with each passing decade.
For those over 90, ED treatment is still possible but requires more caution. Providers may still consider medications like Viagra or Cialis, but they’ll need to carefully review heart health, kidney function, and potential drug interactions first.
The treatment goals remain the same, but safety and individualized care become the top priorities at this age.
Is Viagra safe for seniors?
Viagra’s safe for many seniors, but risks increase with age or certain health issues. Seniors may face higher side effect risks, especially with heart, liver, or kidney problems. Providers often recommend that those aged 65 and up start at 25 mg. Always check with your healthcare provider before using Viagra if you’re older.
Older adults (65 and older) process Viagra differently than younger people. The medication stays in their system longer and reaches higher levels in the blood.
This increases the risk of side effects like headaches, flushing, or dizziness. As a result, healthcare providers often start older adults on a lower 25 mg dose. This can reduce the chance of side effects while still providing benefits.
Your healthcare provider can adjust your dosage based on how you respond to the medication and any other health conditions you may have.
What alternative ED treatments for seniors are available?
When oral medications aren’t enough, seniors can try penile injections or intraurethral suppositories (pellets) like alprostadil, which act quickly and work in up to 80% of cases. An inflatable penile prosthesis is a long-term surgical option with satisfaction rates as high as 90–98%.
Healthcare providers may also adjust or replace medications that interfere with sexual function. Checking testosterone levels is important, especially if symptoms of hypogonadism are present. Losing weight, exercising, and quitting smoking can raise testosterone.
If anxiety or depression is involved, seeing a therapist or sexologist can support both mental health and sexual satisfaction.
What causes ED in senior men?
ED in senior men is primarily caused by aging-related changes to blood vessels and smooth muscle in the penis, though multiple factors often contribute to the condition.
Research estimates that about 70% of men ages 70 and older report being “sometimes able” or “never able” to achieve an erection adequate for satisfactory intercourse, compared with just 30% of older men who report being “usually able” or “always or almost always able.”
Blood vessel problems are the most common reason. As you age, blood vessels in your penis don't work as well. Blood may leak out too quickly, making it hard to keep an erection.
Health conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease become more common with age and can cause inflammation. This damages blood vessels and their ability to relax and increase blood flow, which is necessary to get and keep an erection.
Psychological factors like depression and anxiety can also contribute to ED in older men. Studies show that those with depression are at a higher risk of experiencing ED than those without.
In fact, ED and mood disorders often share overlapping symptoms, and one can worsen the other. Some antidepressants, particularly SSRIs, may also cause or worsen ED as a side effect.
In addition, lifestyle factors like smoking, drinking too much alcohol, and being overweight can make ED worse as you get older.
Your healthcare provider can help find what's causing your ED and recommend the best treatment.
How ED pills work
ED pills help you get and keep erections by improving blood flow to the penis. When you're sexually aroused, your body releases a chemical called nitric oxide that tells the penile blood vessels to relax and fill with blood.
An enzyme called PDE5 breaks down this signal, making your erection go away. ED pills block the PDE5 enzyme, which lets more blood stay in your penis longer.
You still need to be turned on for the pills to work, as they don't create automatic erections, but require sexual stimulation to take effect.
All ED medications work the same basic way, but they differ in how long they last and when you should take them. Your healthcare provider can help you choose which is best for your lifestyle and health needs.
Common side effects of ED medications for seniors
Viagra, Cialis, and other ED medications are safe for most people when taken correctly. However, you might experience some mild side effects, the most common ones being headache, stuffy nose, and facial flushing. Some people also get indigestion or heartburn.
Before you start taking ED medication, talk with your healthcare provider about your health history. This includes any heart conditions (like past heart attacks or heart failure), stroke, stomach ulcers, prostate issues, and all the medications or treatments you're currently using.
Seek emergency medical help right away if you get a painful erection that lasts more than four hours (called priapism). If you don't get treatment quickly, this can permanently damage your penis.
Keep in mind, sexual activity can put stress on your heart, so if you have heart problems or heart disease, ED pills might not be safe for you. And if you have high or low blood pressure, ED medications are usually okay to take, but your healthcare provider might want to check your blood pressure or change your dose to keep you safe.
Be sure to talk to your provider before starting treatment if you have concerns about how ED medication may affect your heart health.
Common interactions with ED medications for seniors
ED medications can interact with other drugs you're taking. While these interactions aren’t specific to older people, seniors may be more likely to face them if they’re taking additional medications. This is why it’s crucial to tell your healthcare provider about everything you take, including prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements.
Viagra should never be taken with nitrates. This includes prescription medications for chest pain (like nitroglycerin) and recreational drugs such as nitrites ("poppers"). Taking sildenafil with nitrates can cause a severe drop in blood pressure.
Certain medications slow down the breakdown of Viagra in the body, leading to higher concentrations and an increased risk of side effects. These CYP3A4 inhibitors include ritonavir, saquinavir, erythromycin, and antifungals (ketoconazole, itraconazole). Grapefruit juice can also similarly impact the CYP3A4 enzyme.
If you take medications for high blood pressure, particularly alpha-blockers such as doxazosin or tamsulosin (used for prostate conditions), Viagra may cause a further drop in blood pressure.
Avoid taking Viagra with other PDE5 inhibitors, such as Revatio (sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension), Cialis, or vardenafil, as this can increase the risk of side effects.
Do not take sildenafil with riociguat, a medication for pulmonary hypertension, due to the risk of dangerously low blood pressure.
Remember that this list doesn't cover everything, so make sure to tell your healthcare provider about all the medications you take.
Bottom line: the 4 best ED drugs for seniors
ED becomes more common with age, but many seniors can still maintain sexual health. Choosing the best ED drug for seniors depends on health, preferences, and potential risks. Here’s what to remember:
Cialis lasts longest: Cialis can stay effective for up to 36 hours and works well for planned or spontaneous sex.
Viagra and vardenafil act faster: These drugs can work within an hour but may only last up to four hours.
Start low, go slow: Seniors often need lower starting doses to avoid stronger side effects and drug interactions.
Health history matters: Heart disease, liver or kidney issues, and other conditions may influence which ED drug is safest, or if alternatives to medication are best.
Talk to your provider: A medical professional can help choose the best ED treatment based on your personal health and goals and help you find a treatment plan that works.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs): the 4 best ED drugs for seniors
What is the best treatment for ED in the elderly?
The best treatment for ED in the elderly depends on the person. Tadalafil and sildenafil are commonly prescribed and effective for many people, but there are other options. Your healthcare provider can determine which treatment works best for your specific health situation and other medications you may be taking.
Can a 70-year-old man take Viagra?
A 70-year-old man can take Viagra, but healthcare providers usually start with a lower 25 mg dose because older adults process the medication differently. The drug stays in your system longer and reaches higher levels in your blood, which can increase side effects.
Your healthcare provider will evaluate your heart health and other medications before prescribing Viagra.
Can a 90-year-old man take Viagra?
A 90-year-old man can potentially take Viagra, but it requires careful medical supervision. At this age, healthcare providers must thoroughly evaluate your cardiovascular health, kidney function, and medication interactions before prescribing any ED treatment.
Safety is the main concern due to the higher likelihood of taking multiple medications and having health conditions that could interact with ED medication.
Can a 70-year-old man still get hard?
A 70-year-old man can still get hard, though ED becomes more common with age. The same ED medications that work for younger men remain effective for men in their 70s. However, healthcare providers may recommend lower starting doses and monitor for drug interactions.
What can a 75-year-old man do to treat erectile dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction at age 75 can be treated using the same PDE5 inhibitor medications available to younger men, including sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and others.
Your healthcare provider will help you determine the best choice and adjust dosages based on your overall health and other medications.
DISCLAIMER
If you have any medical questions or concerns, please talk to your healthcare provider. The articles on Health Guide are underpinned by peer-reviewed research and information drawn from medical societies and governmental agencies. However, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Viagra Important Safety Information: Read more about serious warnings and safety info.
Cialis Important Safety Information: Read more about serious warnings and safety info.
References
DailyMed. (2023). Label: vardenafil tablet, orally disintegrating. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=0ce4eb7b-fa50-441d-ae71-eb33dca27926
Dhaliwal, A. & Gupta, M. (2023). PDE5 Inhibitors. StatPearls. Retrieved on Jul. 15, 2025 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549843/
Ferrini, M. G., Gonzalez-Cadavid, N. F., & Rajfer, J. (2017). Aging related erectile dysfunction-potential mechanism to halt or delay its onset. Translational Andrology and Urology, 6(1), 20–27. doi: 10.21037/tau.2016.11.18. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28217447/
Gareri, P., Castagna, A., Francomano, D., et al. (2014). Erectile dysfunction in the elderly: an old widespread issue with novel treatment perspectives. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2014, 878670. doi: 10.1155/2014/878670. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3976909/
Gökçe, M. İ. & Yaman, Ö. (2017). Erectile dysfunction in the elderly male. Turkish Journal of Urology, 43(3), 247–251. doi: 10.5152/tud.2017.70482. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5562240/
Gong, B., Ma, M., Xie, W., et al. (2017). Direct comparison of tadalafil with sildenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Urology and Nephrology, 49(10), 1731–1740. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1644-5. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5603624/
Higgins, A., Nash, M., & Lynch, A. M. (2010). Antidepressant-associated sexual dysfunction: impact, effects, and treatment. Drug, Healthcare and Patient Safety, 2, 141–150. doi: 10.2147/DHPS.S7634. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3108697/
Huang, S. A. & Lie, J. D. (2013). Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) Inhibitors In the Management of Erectile Dysfunction. P & T : A Peer-Reviewed Journal for Formulary Management, 38(7), 407–419. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3776492/
Liu, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2018). Erectile Dysfunction and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 15(8), 1073-1082. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2018.05.016. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29960891/
Maiorino, M. I., Bellastella, G., & Esposito, K. (2015). Lifestyle modifications and erectile dysfunction: what can be expected?. Asian Journal of Andrology, 17(1), 5–10. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.137687. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4291878/
Mulhall, J. P., Luo, X., Zou, K. H., et al. (2016). Relationship between age and erectile dysfunction diagnosis or treatment using real-world observational data in the USA. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 70(12), 1012–1018. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12908. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5540144/
Saramies, J., Koiranen, M., Auvinen, J., et al. (2022). A Natural History of Erectile Dysfunction in Elderly Men: A Population-Based, Twelve-Year Prospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(8), 2146. doi: 10.3390/jcm11082146. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35456238/
Selvin, E., Burnett, A. L., & Platz, E. A. (2007). Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in the US. The American Journal of Medicine, 120(2), 151–157. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.06.010. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17275456/
Sharlip, I.D., Shumaker, B.P., Hakim, L.S., et al. (2008). tadalafil is efficacious and well tolerated in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) in men over 65 years of age: results from Multiple Observations in Men with ED in National tadalafil Study in the United States. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 5(3), 716-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00712. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18304286/
U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA-a). (2018). Highlights of prescribing information: Cialis (tadalafil) tablets, for oral use. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021368s030lbl.pdf
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA-b). (2018). Highlights of prescribing information: STENDRA (avanafil) tablets, for oral use. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/202276s018lbl.pdf
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2017). Highlights of prescribing information: Viagra (sildenafil citrate) tablets, for oral use. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/020895s048lbl.pdf












