Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
There are natural changes in estrogen levels throughout our lifetimes and our menstrual cycles, but when they drop too low or rise too high, that can lead to health problems down the line. Read all about the hormone (and why it’s so important) below.
What is estrogen and why is it important?
Estrogens are a group of sex hormones that are more prominent in people with ovaries. They include estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3), and they’re produced by the ovaries, the adrenal gland (a little gland on top of each kidney), and the placenta during pregnancy.
At puberty, estrogen leads to the growth of breasts, pubic and underarm hair, and kicks off (and later helps control) menstrual cycles.
Estrogen also plays a role in keeping cholesterol levels in check, maintaining bone health, and producing hormones that affect our brains, hearts, and skin (among other parts of our bodies).
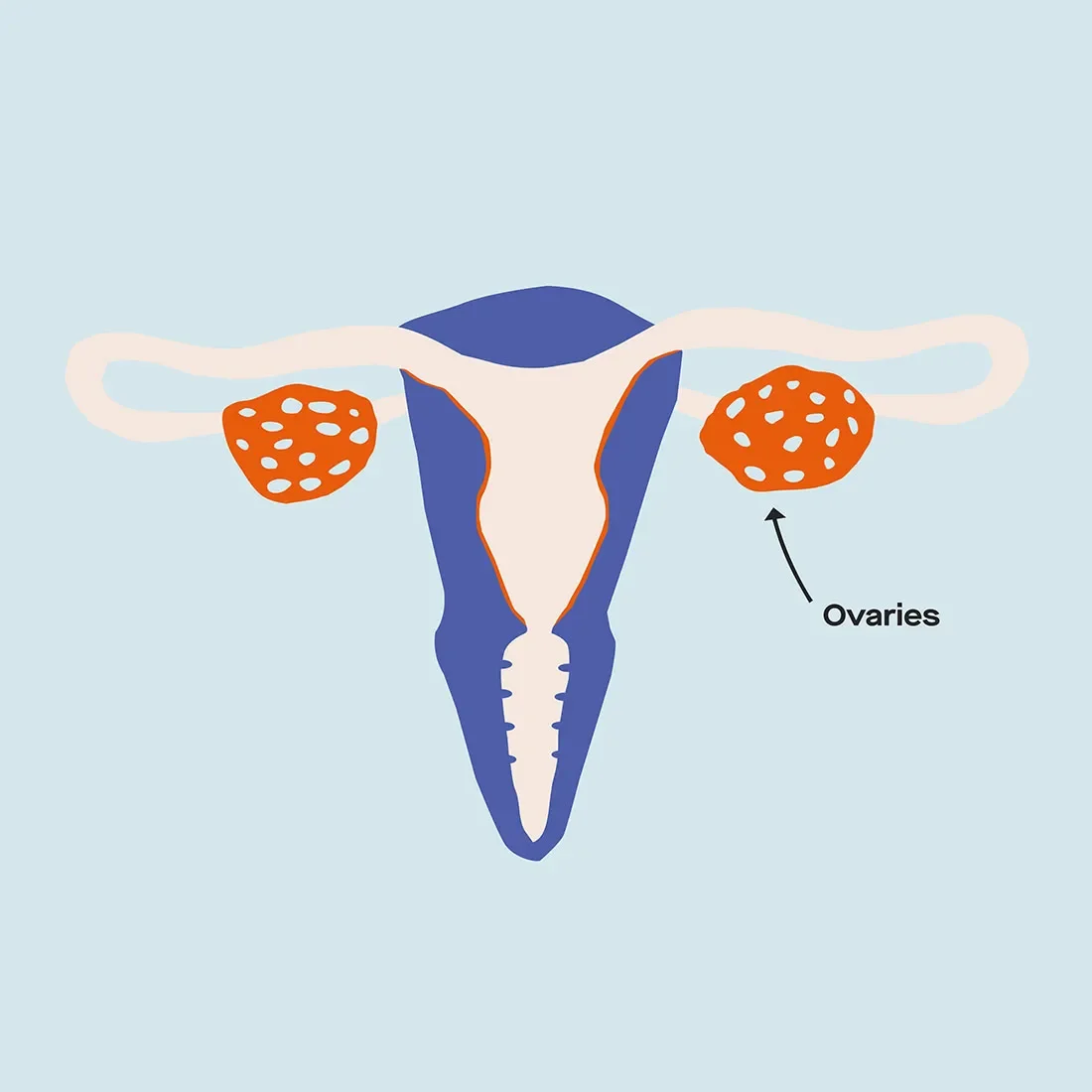
Estrogen is produced in the ovaries, the adrenal gland, and the placenta during pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of low estrogen?
First, let’s talk about causes. Women may have lower levels of estrogen after they hit menopause, after an oophorectomy (surgical removal of the ovaries), or when they have a lower body-fat percentage.
If you have lower levels of estrogen, you might experience:
Infrequent or disrupted periods
Hot flashes and/or night sweats
Sleeping issues
Decreased sexual desire
Mood swings
Dry skin
Menstrual migraines
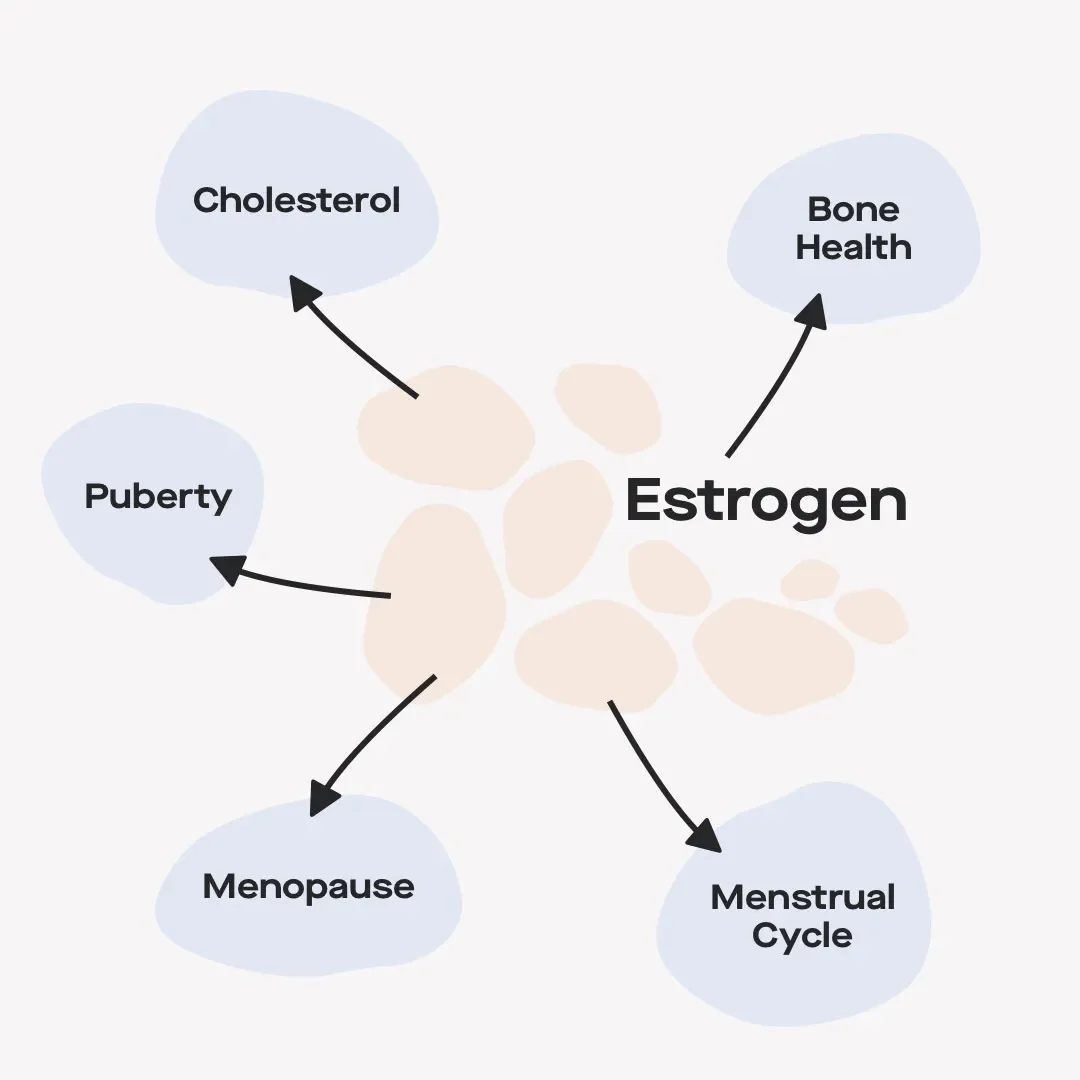
Estrogen can affect many parts of a woman’s body
What are the symptoms of high estrogen?
Women can have higher levels of estrogen (aka estrogen dominance) if they use hormonal birth control that contains estrogen or if they have a higher body-fat percentage.
If you have higher levels of estrogen, you might experience:
Weight gain
Changes in your period
Worsening of premenstrual syndrome
Non-cancerous breast lumps
Uterus fibroids
Fatigue
Decreased sex drive
Anxiety or depression
How do estrogen levels change with age?
During reproductive years, estrogen levels naturally fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle — they're highest toward the middle and lowest during your period.
At the onset of menopause, when periods come to a complete stop, estrogen levels drop.
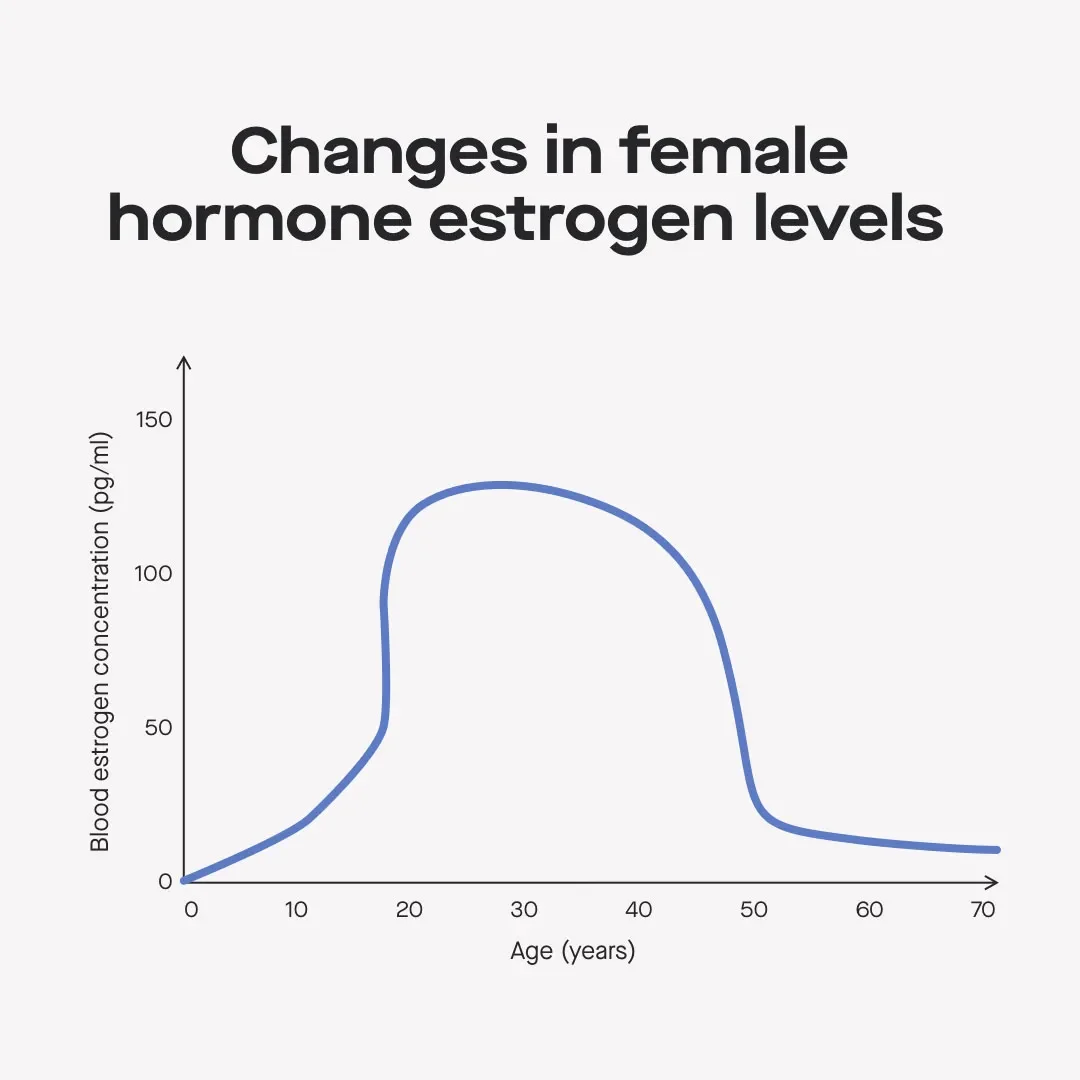
Estrogen levels change over time.
DISCLAIMER
If you have any medical questions or concerns, please talk to your healthcare provider. The articles on Health Guide are underpinned by peer-reviewed research and information drawn from medical societies and governmental agencies. However, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
References
Jasuja, G. K., Travison, T. G., Davda, M., Murabito, J. M., Basaria, S., Zhang, A., Kushnir, M. M., Rockwood, A. L., Meikle, W., Pencina, M. J., Coviello, A., Rose, A. J., D'Agostino, R., Vasan, R. S., & Bhasin, S. (2013). Age trends in estradiol and estrone levels measured using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in community-dwelling men of the Framingham Heart Study. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences , 68 (6), 733–740. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls216