Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
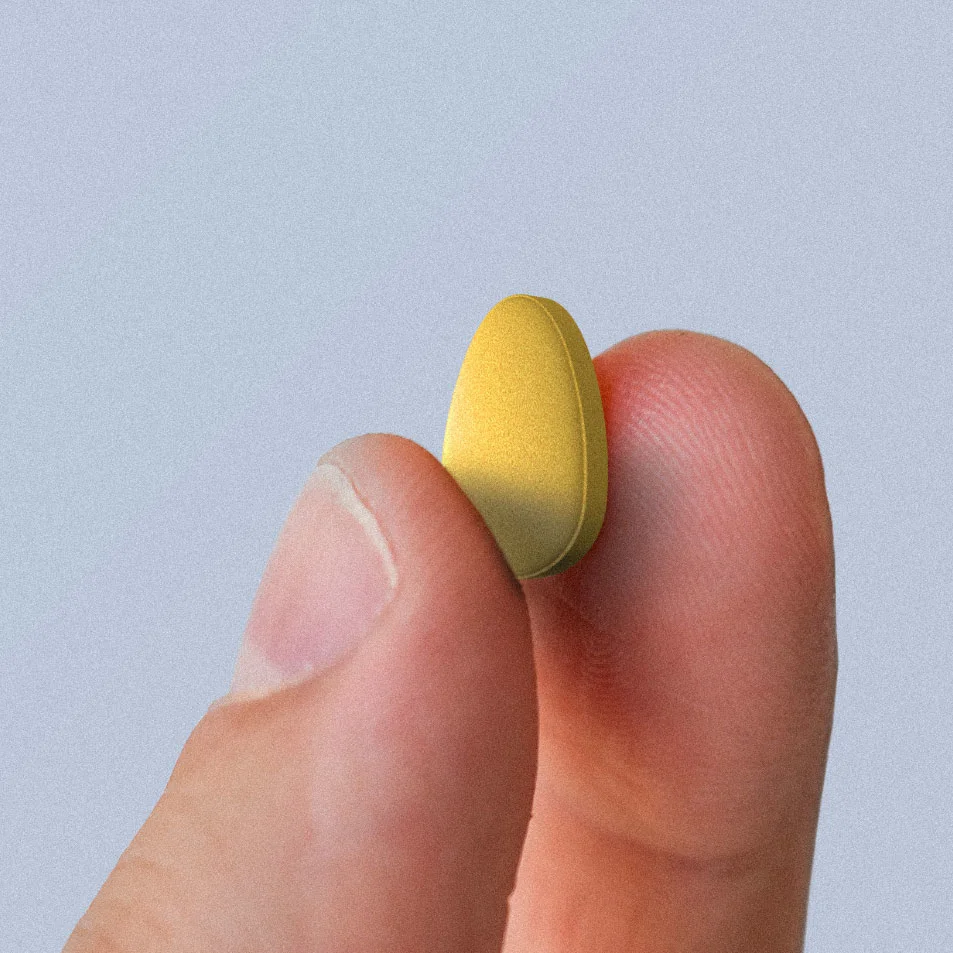
Sildenafil 20mg is a dosage approved to treat a lung condition called pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), but it’s also prescribed to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). Sildenafil is the active ingredient in Viagra (the generic of Viagra is called sildenafil), a popular ED medication usually prescribed in doses of 25mg, 50mg, or 100mg. Healthcare providers sometimes also prescribe sildenafil 20mg to treat erectile dysfunction if a low dosage is the best treatment option for that person.
Continue reading to learn if sildenafil 20mg is the right treatment for you.
What is sildenafil 20mg?
Sildenafil (brand name Revatio) is typically used as a treatment for a lung condition called pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The medication works by relaxing blood vessels to improve blood flow. Consequently, sildenafil can be used to treat erectile dysfunction for the same reason. Improved blood flow to the penis means harder erections for more satisfying sex.
The FDA approved sildenafil 20mg for the treatment of PAH and the 25mg, 50mg, and 100mg dosages for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Because sildenafil is the active ingredient in Viagra, the 20mg dose can be prescribed off-label to treat ED (DailyMed, 2020).
Why use sildenafil 20mg?
If your healthcare provider is considering prescribing sildenafil for the treatment of ED, the traditional starting dose is 50mg. But this dose might not be effective for everyone, and a higher dose may mean a higher risk of side effects for some people. Since the generic of Viagra is only available in dosages of 25mg, 50mg, and 100mg, the prescribing options are limited. Clinicians can opt to prescribe 20mg sildenafil (or multiples of 20mg) to give their patients a more precise dose.
Money is also a consideration when deciding between Viagra or sildenafil. Brand name Viagra is expensive and can cost upwards of $70 per dose. Opting for the generic of Viagra (sildenafil) lowers the price, and opting for generic Revatio in 20mg increments may be an even more pocket-friendly option.
So why would you want to take 20mg sildenafil when 25mg is available? Here are some possible reasons:
Your healthcare provider may want to start you at 20mg to see how you respond to the medication.
You might experience side effects on 25mg or 50mg, but less so (or not at all) on 20mg or 40mg.
50mg might not be as effective as 60mg for you, and you and your health provider agree a slightly higher dose is better.
As a rule of thumb, it's best to take the lowest effective dose of a drug in order to avoid potential side effects. Prescribing sildenafil in 20mg increments can make it easier for your healthcare provider to find the dose that's best for you—one that maximizes sildenafil's benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
Sildenafil 20mg: How long does it last?
Sildenafil starts working within 30–60 minutes, and typically works for about four hours, so you should plan accordingly. Keep in mind that the drug doesn’t instantly give you an erection. Instead, it helps you get and maintain an erection when you get aroused (Smith, 2022).
If you’ve taken a dose of Viagra and it doesn’t work, do not take another dose before 24 hours have passed. If you find that the dosage you’ve been prescribed isn’t effective, talk to your healthcare provider about trying a higher dose or a different medication altogether.
Viagra alternatives
While Viagra is typically an effective treatment for erectile dysfunction, there are other similar medications that might be better treatment options for you. Other ED medications include:
Vardenafil (brand name Levitra)
Avanafil (brand name Stendra)
Sildenafil and other ED medications are PDE5 inhibitors, which work by suppressing an enzyme called PDE5, a.k.a. an erection's "off switch." The "on switch" is a natural chemical called cGMP, which tells blood vessels in the penis to dilate and fill with blood. PDE5 breaks down cGMP, allowing blood to flow out of the penis. When PDE5 is blocked, blood vessels in the penis stay dilated. This makes erections stay harder for longer (Dhaliwal, 2022).
Although PDE5 inhibitors all work on the same natural chemical—PDE5—that doesn't mean they're all the same. Sildenafil may take 30 minutes to work and may last for 4 to 5 hours. Avanafil can be taken 15 minutes before sexual activity, and it remains effective for about the same time as sildenafil. Tadalafil comes in two formulations: one is taken daily, the other as needed and can be effective for up to 36 hours.
Picking the right medication for you might involve a little bit of back and forth with your provider, but if a medication isn’t working as well as you would like, let them know. Getting the right medication and the right dosage can improve your sex life significantly.
Have better sex with Ro
What causes ED?
ED—when you can't get or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfying sex—is the most common sexual dysfunction in men. Experts believe that around 30–50 million American men have experienced ED at some point. ED can happen at any age, but it becomes more common as men age. By the time a man is in his 40s, he has about a 40% chance of having experienced ED at some point. That likelihood increases by about 10% for each successive decade of life (Sooriyamoorthy, 2022; Ferrini, 2017).
That said, ED is not considered a "natural" part of aging. It’s important to know that many different underlying health conditions can contribute to it, and that addressing those conditions can often help improve symptoms of ED. These conditions include:
Nerve damage
Sleep apnea
That's why it's important to check in with a healthcare provider at the first sign of ED. They'll evaluate your medical history, gauge your overall health, and can catch any potential health issues so you can get the treatment you need.
How to get Viagra (sildenafil)
Viagra (sildenafil) is not available over the counter, but you can consult with a healthcare provider in person or online to get a prescription. There are more options available than ever to receive Viagra discreetly in the mail, if this is a concern.
When buying sildenafil online, beware of counterfeiters. You've seen them: At some point in your web-surfing history, you've probably wandered into an explosion of pop-up ads hawking Viagra for mere cents on the dollar. Many of the establishments behind these ads are not legit, and the product they sell can be dangerous.
In 2011, Pfizer, the manufacturer of Viagra, investigated counterfeits by buying them online and testing their contents. Some of the pills they received contained blue printer ink, amphetamines ("speed"), an antibiotic called metronidazole, too much of the active ingredient sildenafil (or not enough), and drywall (Pfizer, n.d.).
Side effects and warnings
Side effects associated with sildenafil and other ED medications include headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion, stomach upset, backache, and (rarely) temporary impaired color vision. If you experience vision changes, chest pain, or priapism (an erection lasting more than four hours) seek medical attention immediately.
Sildenafil and other PDE5 inhibitors should never be taken with nitrates or nitrites. These include prescription medications used to treat chest pain and a recreational drug called poppers. Taking sildenafil with nitrates can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure that could be fatal.
If you're interested in taking sildenafil to treat ED, make an appointment with your healthcare provider. Your provider will help you find a medication and dosage that works for you.
DISCLAIMER
If you have any medical questions or concerns, please talk to your healthcare provider. The articles on Health Guide are underpinned by peer-reviewed research and information drawn from medical societies and governmental agencies. However, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Viagra Important Safety Information: Read more about serious warnings and safety info.
Cialis Important Safety Information: Read more about serious warnings and safety info.
References
Barnett, C. F. & Machado, R. F. (2006). Sildenafil in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Vascular Health and Risk Management, 2 (4), 411–422. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.4.411. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1994020/
DailyMed. (2020). SILDENAFIL tablet. Retrieved from https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=15372a7c-2935-48dc-a55a-8966719b50be
Dhaliwal. A. & Gupta, M. (2022). PDE5 inhibitors. StatPearls . Retrieved on Dec. 14, 2022 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549843/
Eardley, I., Ellis, P., Boolell, M., & Wulff, M. (2002). Onset and duration of action of sildenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 53 . doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.00034.x. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1874251/
Ferrini, M. G., Gonzalez-Cadavid, N. F., & Rajfer, J. (2017). Aging related erectile dysfunction-potential mechanism to halt or delay its onset. Translational Andrology and Urology , 6 (1), 20–27. doi: 10.21037/tau.2016.11.18, Retrieved from https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/13319/13808
Nunes, K. P., Labazi, H., & Webb, R. C. (2012). New insights into hypertension-associated erectile dysfunction. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 21 (2), 163–170. doi: 10.1097/mnh.0b013e32835021bd. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22240443/
Pfizer. (n.d.). Viagra: Avoid counterfeits. Retrieved on Dec. 14, 2022 from https://www.viagra.com/avoid-counterfeits
Smith, B. P. & Babos, M. (2022). Sildenafil. StatPearls . Retrieved on Dec. 14, 2022 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558978/
Sooriyamoorthy, T. & Leslie, S. W. (2022). Erectile dysfunction. StatPearls. Retrieved on Dec. 14, 2022 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562253/