Key takeaways
Sildenafil and tadalafil are both prescription medications used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) by improving blood flow.
Tadalafil is also used to manage benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Sildenafil lasts about four hours, while tadalafil lasts up to 36 hours.
Both medications start working in about 30 minutes.
Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
Key takeaways
Sildenafil and tadalafil are both prescription medications used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) by improving blood flow.
Tadalafil is also used to manage benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Sildenafil lasts about four hours, while tadalafil lasts up to 36 hours.
Both medications start working in about 30 minutes.
When it comes to treating erectile dysfunction (ED), two of the most well-known medications are sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis). Both are PDE5 inhibitors, a type of medication that boosts blood flow to help you get and maintain an erection. But they differ in how fast they work and how long they last.
Let’s break down the key differences to help you choose the right fit.
Sildenafil vs. tadalafil compared: which is better for ED?
Sildenafil | Tadalafil | |
Brand-name version | Viagra | Cialis |
Onset | 30–60 minutes | 30 minutes |
Duration | Around 4–6 hours | Up to 36 hours |
Dosing options | As-needed | As-needed or daily (depending on the dosage) |
Food interactions | High-fat meals may delay effects | None |
Flexibility | Requires timing with sexual activity | Allows more spontaneous sexual activity, especially when taken daily |
Common side effects | Headache, flushing, nasal congestion, visual changes, indigestion | Headache, indigestion, back pain, muscle aches |
Maximum dose | 100 mg | 20 mg (taken as needed) |
Sildenafil vs. tadalafil: which works faster?
Both sildenafil and tadalafil start working in about 30–60 minutes, but sildenafil’s onset can be delayed by a high-fat meal.
Sildenafil is usually taken about an hour before sex. However, you can take it anywhere from 30 minutes to four hours beforehand, depending on how your body responds.
Tadalafil also begins working within 30 minutes (as quickly as 20 minutes, for some people) and isn’t affected by food. Its effects can last up to 36 hours, so you have a wider window for sexual activity.
If you’re prescribed daily tadalafil, you don’t need to time your medication based on planned sexual activity. Just take it at the same time each day to maintain steady levels.
Sildenafil vs. tadalafil: which lasts longer?
Tadalafil lasts up to 36 hours — much longer than sildenafil, which works for about 4–6 hours.
Because sildenafil provides a shorter window of effectiveness, it’s typically best for planned sexual activity. You should only take your ED medication as prescribed, no more than once per day.
Tadalafil, on the other hand, stays active for up to 36 hours, so there’s no need to plan your timing as carefully. Its lower doses also come as a daily option, which keeps a steady amount in your system so you can be ready whenever the moment feels right.
Sildenafil vs. tadalafil: cost comparison
Generic sildenafil (100 mg) typically costs about $2–$29 for 30 tablets. Generic tadalafil (5 mg) typically costs around $2–$29 for 30 tablets with discounts.
Without insurance or discounts, retail prices can climb quickly — as much as $440 for sildenafil and $261 for tadalafil. That said, savings programs and coupons, such as those available on sites like GoodRx and SingleCare, can make both drugs much more affordable.
Brand-name Viagra and Cialis are far pricier, often running over $689 and $314, respectively, depending on where you live, even with discounts.
Sildenafil vs. tadalafil: dosage and schedules
Healthcare providers usually prescribe sildenafil at a starting dose of 50 mg or 100 mg to be taken as-needed about an hour before sex. Tadalafil typically starts at 10–20 mg as needed or 2.5–5 mg daily for ongoing use.
Of course, starting doses may vary depending on factors like your age or other health conditions. Be sure to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely.
You should only take one dose of sildenafil in a 24-hour period, about 30–60 minutes before sexual activity. If you notice side effects, your healthcare provider may adjust your dosage accordingly.
Tadalafil comes in several forms and strengths: 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg tablets. It can be taken as needed or, for the lower doses, daily to maintain steady levels in your system.
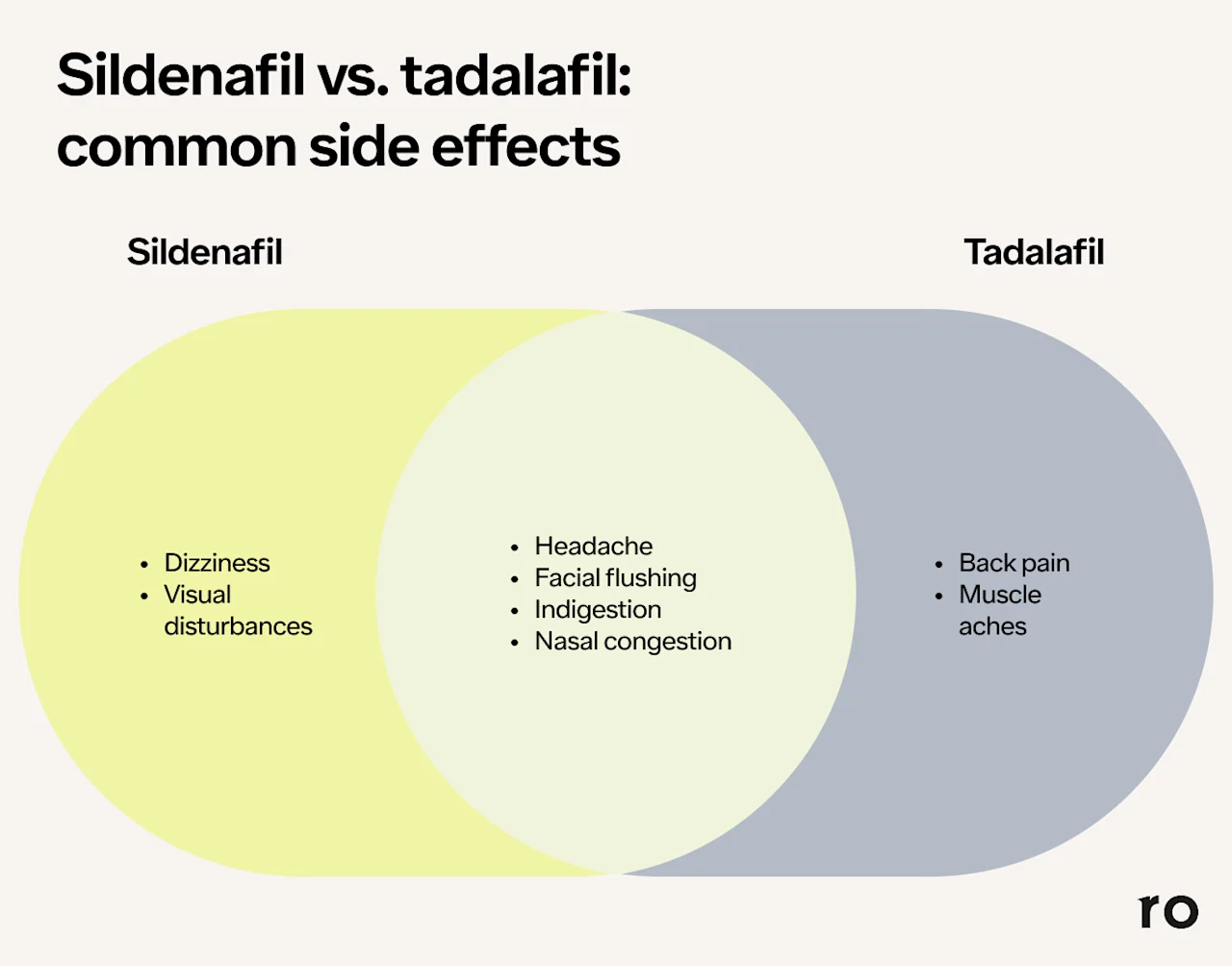
Sildenafil vs. tadalafil: side effects
Studies show that sildenafil and tadalafil are generally both safe and effective for treating ED. However, many people prefer tadalafil. That’s because it lasts longer, allows for more spontaneity, and can even boost sexual confidence.
Here’s a quick look at the most common side effects for each.
Sildenafil side effects
Common side effects of sildenafil include:
Headache
Facial flushing
Indigestion
Nasal congestion
Dizziness
Visual changes (such as a blue tint or other color disturbances)
Most sildenafil side effects are mild and short-lived. Still, if you ever have serious symptoms — especially an erection lasting longer than four hours — get medical help right away.
Avoid taking sildenafil if you’re using nitrates (like nitroglycerin for chest pain) or nitrites (“poppers”). This combo can make your blood pressure dangerously low. It also shouldn’t be used with guanylate cyclase stimulators (like riociguat).
These aren’t the only medications that can potentially interact with sildenafil. Before starting sildenafil, talk with your healthcare provider to make sure it’s safe for you, especially if you have heart, circulation, or blood pressure issues.
Tadalafil side effects
The side effects of tadalafil can be less common or milder than those seen with sildenafil for some people. They also often improve as you adjust to the medication.
The most common side effects to look out for include:
Headache
Indigestion
Back pain
Muscle aches
Nasal congestion
Facial flushing
Similar to sildenafil, avoid taking this medication if you use nitrates or guanylate cyclase stimulators. You should also skip tadalafil if you’ve had a serious allergic reaction to it or any of its ingredients.
These aren’t the only reasons to avoid tadalafil. Before starting tadalafil, let your healthcare provider know about all medications, supplements, and health conditions you have so they can determine if tadalafil is the right choice for you.
Bottom line
Sildenafil and tadalafil are commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED), among other conditions. They belong to the same drug class and work by increasing blood flow in certain areas of the body.
Sildenafil (Viagra) works quickly and is best for planned sex. It’s taken as needed about an hour before sexual activity.
Tadalafil (Cialis) lasts up to 36 hours, making it ideal for more spontaneity. It can be taken as needed or at a lower dosage for daily use.
Both treat ED, and tadalafil can also help with BPH (enlarged prostate) symptoms when it is taken at a low-level daily dose.
Some men prefer sildenafil for its shorter window, while others choose tadalafil for its flexibility and longer effect.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Which is better: tadalafil or sildenafil?
Whether tadalafil or sildenafil is better is an individual decision that depends on your lifestyle and preferences.
Sildenafil works for a few hours and is best for planned sex since you take it about 30–60 minutes beforehand.
Tadalafil lasts up to 36 hours and can be taken as needed or daily, giving you more flexibility and spontaneity.
Many people prefer tadalafil for its longer-lasting effects, but both medications are highly effective for ED.
Is 20 mg tadalafil equal to 100 mg Viagra?
Not exactly. Tadalafil’s max recommended dose is 20 mg, and sildenafil’s max recommended dose is 100 mg. But those numbers don’t directly compare since the two drugs differ in timing and how long they last. Both are designed to help you get and keep an erection, just with different dosing schedules and durations of effect.
Does tadalafil keep you hard after coming?
No, tadalafil doesn’t keep you hard after coming. In other words, it doesn’t cause nonstop erections. Rather, tadalafil helps you get an erection when you’re sexually stimulated, but it doesn’t override your body’s natural recovery period after orgasm. Because it stays in your system for up to 36 hours, though, it may help you get hard again sooner if you’re aroused later.
Which is better for BPH: sildenafil or tadalafil?
Tadalafil is the better pick for BPH. It’s the only ED medication that’s also FDA-approved to treat enlarged prostate symptoms, helping relax muscles in the bladder and prostate to make urination easier. Plus, since it also treats erectile dysfunction, it’s a convenient two-in-one option for men managing both conditions — something sildenafil doesn’t offer.
What is sildenafil?
Sildenafil (the active ingredient in Viagra) is an FDA-approved PDE5 inhibitor used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). It improves blood flow to help with erections and is taken as needed before sexual activity.
What is tadalafil?
Tadalafil (the active ingredient in Cialis) is another FDA-approved PDE5 inhibitor that treats ED, PAH, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It lasts longer than sildenafil (up to 36 hours) and can be taken as needed or daily for more flexibility.
DISCLAIMER
If you have any medical questions or concerns, please talk to your healthcare provider. The articles on Health Guide are underpinned by peer-reviewed research and information drawn from medical societies and governmental agencies. However, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Viagra Important Safety Information: Read more about serious warnings and safety info.
Cialis Important Safety Information: Read more about serious warnings and safety info.
References
Asclemed USA, Inc. (2023). Prescribing Information: Tadalafil - tadalafil tablet, film coated. Retrieved from https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/51f87c9b-038c-4793-b0d5-5359ae231074/spl-doc
Bakry, A. R., Mahran, A. M., Gaber, H. D., Sedek, M. I., GamalEl Din, S. F., Motawi, A. T., Mohamed, M. D., & Elshebany, A. (2024). Evaluation of the effect of daily tadalafil 5 mg versus daily sildenafil 25 mg on neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratios in patients with erectile dysfunction: A comparative randomized controlled study. Archivio italiano di urologia, andrologia : organo ufficiale [di] Societa italiana di ecografia urologica e nefrologica, 96(4), 12756. https://doi.org/10.4081/aiua.2024.12756. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39692427/
Dhaliwal, A. & Gupta, M. (2023). PDE5 inhibitors. StatPearls. Retrieved on Feb. 16, 2025 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549843/
Eli Lilly and Company. (2023). Prescribing Information: Cialis - tadalafil tablet, film coated. Retrieved from https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=bcd8f8ab-81a2-4891-83db-24a0b0e25895&type=display
Fahmy, G. & Hess, J. (2024). Tadalafil. StatPearls. Retrieved on Feb. 16, 2025 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK603743/
GoodRx-a. (n.d.). Cialis. Retrieved from https://www.goodrx.com/cialis?srsltid=AfmBOop7caXf_3d8Gb9fZ-z9Tm-q95DuSzgj-VAJcBugJS1tuAERM680&label_override=cialis
GoodRx-a. (n.d.). Sildenafil 100mg tablet: Generic Viagra used for erectile dysfunction. Retrieved from https://www.goodrx.com/viagra
GoodRx-b. (n.d.). Tadalafil (Cialis) 5mg tablets: Generic Cialis used for erectile dysfunction. Retrieved from https://www.goodrx.com/tadalafil-cialis
GoodRx-a. (n.d.). Viagra. Retrieved from https://www.goodrx.com/viagra?label_override=viagra
Govier, F., Potempa, A. J., Kaufman, J., et al. (2003). A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, crossover study of patient preference for tadalafil 20 mg or sildenafil citrate 50 mg during initiation of treatment for erectile dysfunction. Clinical Therapeutics, 25(11), 2709–2723. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(03)80328-4. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14693299/
Huang, S. A. & Lie, J. D. (2013). Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors In the management of erectile dysfunction. P & T: A Peer-Reviewed Journal for Formulary Management, 38(7), 407–419. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3776492/
Pfizer. (2017). Prescribing Information: Viagra - sildenafil citrate tablet, film coated. Retrieved from https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=0b0be196-0c62-461c-94f4-9a35339b4501&type=display
SingleCare-a. (n.d.). Sildenafil Citrate 100mg tablet: Generic for: Viagra. Retrieved on Feb. 16, 2025 from https://www.singlecare.com/prescription/sildenafil-citrate?q=Sildenafil%20Citrate%20(Viagra)
SingleCare-b. (n.d.). Tadalafil 5mg tablet: Generic for: Cialis. Retrieved on Feb. 16, 2025 from https://www.singlecare.com/prescription/tadalafil?q=Tadalafil%20(Cialis)
Smith, B. P. & Babos, M. (2023). Sildenafil. StatPearls. Retrieved on Feb. 16, 2025 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558978/
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Limited. (2024). Prescribing information: Sildenafil Citrate - sildenafil tablet, film coated. Retrieved from https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=b48630b1-5208-4d00-b56f-21701f223758&type=display
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2025). Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/ob/index.cfm
U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2023). Tadalafil. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a604008.html












