Here's what we'll cover
Here's what we'll cover
Anxiety is one of the most commonly diagnosed mental health conditions. By some estimates, roughly 32% of Americans will develop an anxiety disorder at some point in their lifetimes (Garakani, 2020; NIMH, 2007).
There are many different ways to treat an anxiety disorder. These include psychotherapy and many relaxation techniques. Anxiety medications can also help, whether taken alone or used alongside another type of anxiety treatment (Chand, 2021).
In this guide, you’ll find a list of common anti-anxiety medications. Keep in mind that not all of these drugs are appropriate for all forms of anxiety or for all people. Every brain is unique. A drug that helps one person with anxiety may not work the same way for you.
Also, you may notice that many of these anti-anxiety drugs are also used to treat depression. This is because some of the same brain systems and neurochemicals that play a role in anxiety also seem to be involved in depression (Garakani, 2020).
Types of anti-anxiety medications
There are a few different types of medications used to treat anxiety. Here are the most common.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter (basically, a brain chemical) that seems to promote positive mood and emotions.
SSRIs block the brain’s nerve cells from absorbing serotonin, which is a process known as “reuptake.” By blocking this reuptake, it’s thought that the brain’s levels of serotonin get a boost. And there’s a lot of evidence that this helps relieve anxiety symptoms (NHS, 2018).
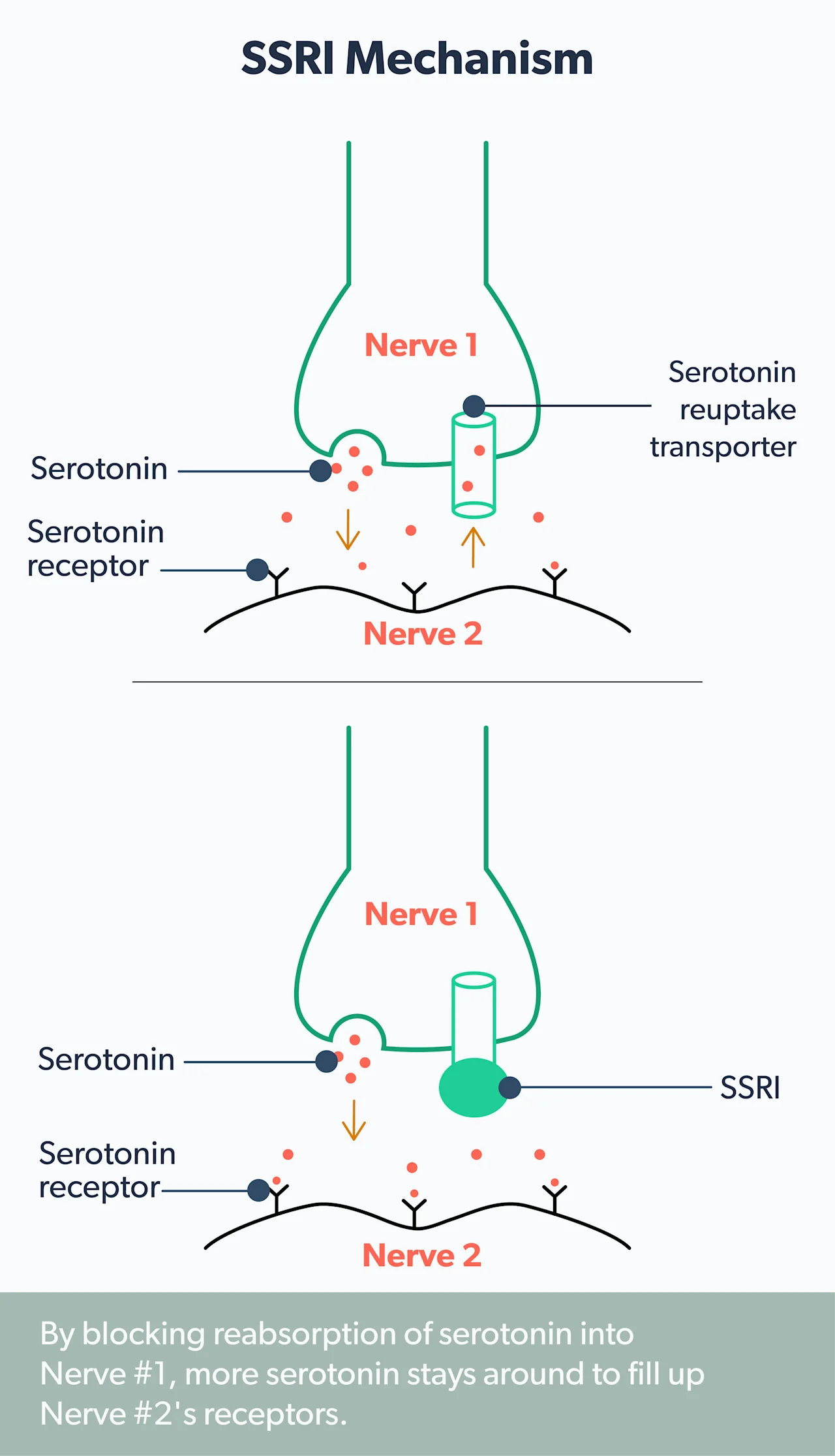
Some of the most common SSRIs are (Chand, 2021):
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
Sertraline (Zoloft)
Paroxetine (Paxil)
Escitalopram (Lexapro)
Citalopram (Celexa)
SSRIs are popular in part because they don’t mess with the activity of other brain chemicals. Like all drugs, they do have side effects. But these tend to be minor compared to many other anti-anxiety medications (Chu, 2021).
Some side-effects of SSRIs include (Chu, 2021):
Sexual dysfunction
Sleep problems
Weight changes
Dizziness
Dry mouth
Headache
Upset stomach
SSRIs don’t start to work immediately. It usually takes at least two weeks before you’ll feel any benefits and it might take up to six weeks until you feel the full effects of the drug (Taylor, 2006). However, some of the side effects can come on right away (Bandelow, 2017).
SSRIs are prescribed for all forms of anxiety and are considered a “first-line” treatment (Chand, 2021). How long you’re taking the drugs can vary. A healthcare provider might recommend you take SSRIs for up to a year or two if they work well for you (Garakani, 2020; Bystritsky, 2021).
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
Norepinephrine, like serotonin, is another brain chemical that seems to play a role in mood and anxiety. SNRIs block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. And there’s evidence that these work well for some people with anxiety (Sheffler, 2021).
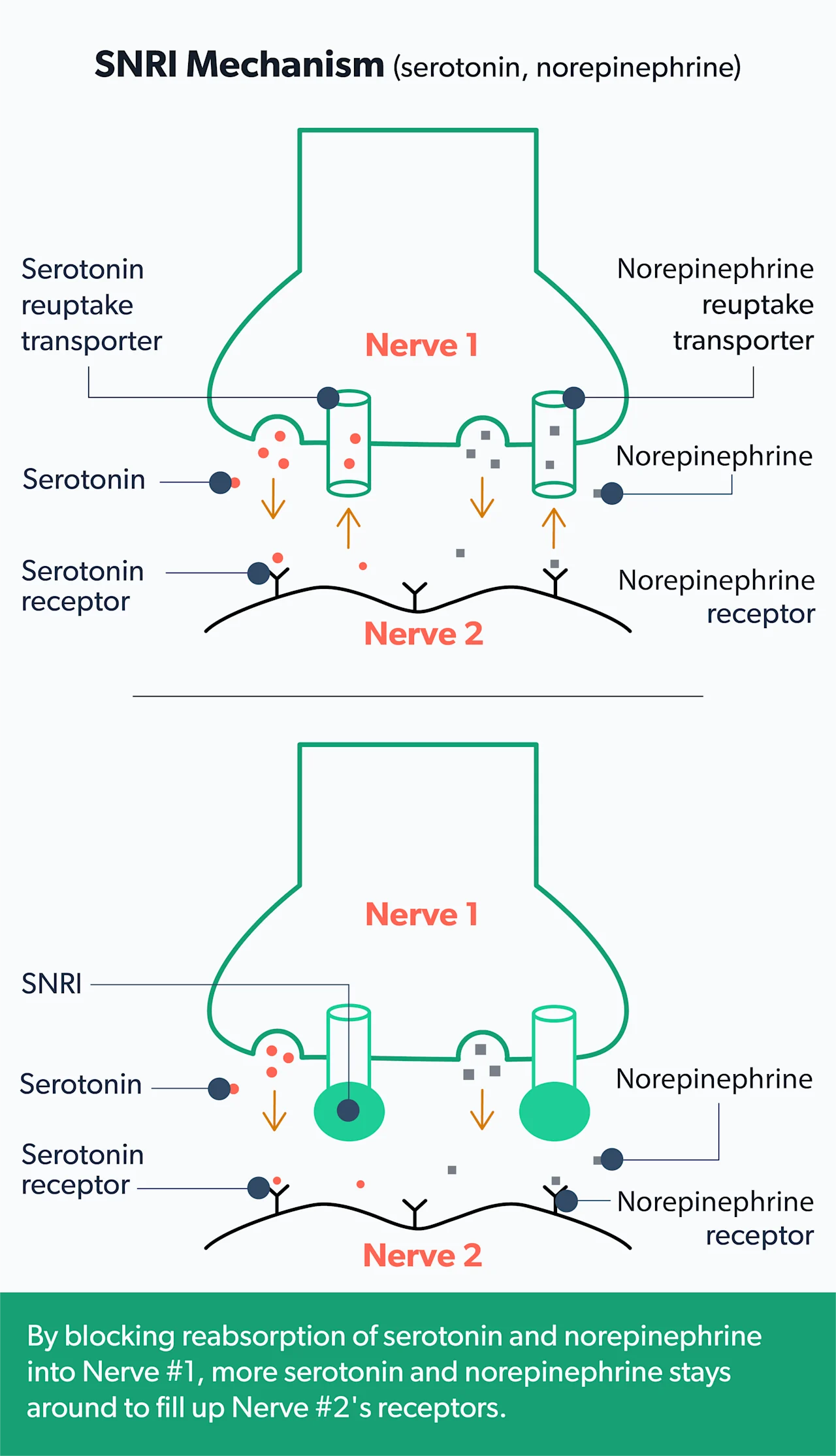
Some of the most common SNRIs are venlafaxine (Effexor XR) and duloxetine (Cymbalta) (Chand, 2021).
Side effects of these and other SNRI drugs include (Bandelow, 2017):
Jitteriness
Nausea
Restlessness
Headaches
Fatigue
Weight gain or loss
Sweating
Sexual dysfunction
Diarrhea
Like SSRIs, SNRIs don’t start to work immediately. While side-effects may show up right away, anxiety benefits tend to take at least a couple of weeks (Bandelow, 2017). Some research has shown that SNRIs work well for treatment lasting six months and longer (Rickels, 2010).
SNRIs are also considered first-line treatment—specifically for generalized anxiety disorders (Chand, 2021). But some of the side effects such as nausea and dry mouth may be more pronounced than those associated with SSRIs (Santarsieri, 2015).
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines, or “benzos,” have been a mainstay of anxiety treatment for decades. Along with SSRIs and SNRIs, they remain one of the most commonly prescribed classes of anti-anxiety drugs (Garakani, 2020).
Benzos can help reduce anxiety—often very quickly. They start to work in as little as 30 minutes, and they tend to reduce muscle tension and other symptoms of anxiety. For this reason, they’re popular as a short-term anxiety treatment or for people who are in the midst of a panic attack or other severe bout of anxiety (Chand, 2021).
Some common benzodiazepines include:
While benzodiazepines are popular and often effective, there’s some evidence that they’re more likely than other anti-anxiety drugs to lead to addiction or abuse. This is one of the reasons why benzos are not considered the go-to medication for anxiety anymore. Today, healthcare providers prefer to prescribe benzos in combination with other anti-anxiety drugs, like SSRIs (Garakani, 2020).
Other side-effects of benzos include (Vashchinkina, 2014):
Memory problems
Dizziness
Clumsiness or falls
Confusion
Sleepiness
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
Like SNRIs, tricyclic antidepressants help increase the brain’s circulating levels of serotonin and norepinephrine. But they do this in slightly different ways than SNRIs (Garakani, 2020).
While there’s evidence that TCAs can help treat anxiety, these drugs have been around since the 1950s (Gillman, 2007). They tend to cause harsher side-effects than SSRIs, SNRIs Is and other, newer anti-anxiety medications. For that reason, medical providers don’t often prescribe them anymore (Garakani, 2020).
TCAs are not FDA approved for the treatment of most anxiety disorders, although there are some special cases when they may still be helpful—for example, when SSRIs or other drugs don’t work well (Garakani, 2020).
Side effects of these drugs include (Garakani, 2020):
Weight gain
Dry mouth
Sleepiness
Urinary problems
Irregular heartbeat
Beta-blockers
These drugs reduce tension, a racing heart, and the other physical symptoms of anxiety. Two common types are propranolol and atenolol (Chand, 2021).
Beta-blockers aren’t FDA-approved for the treatment of anxiety. But medical providers still prescribe beta-blockers in some cases. They’re especially common for people who have specific fears (phobias), such as a fear of public speaking or a fear of spending time in social situations (Chand, 2021).
These drugs work by binding to beta receptors that normally bind to epinephrine and other chemicals associated with increased nervous system activity. By blocking the action of these chemicals, the heart slows, muscles relax, and the nervous system mellows out (Farzam, 2021).
On the other hand, beta-blockers can cause side effects. These include (Farzam, 2021):
Low blood pressure
Fatigue or sleepiness
Dizziness
Nausea
Constipation
Sexual dysfunction
Along with anxiety, beta-blockers can help treat a range of medical conditions. This list includes heart disease, tremors, glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, and many others. If a person has one or several of these conditions, as well as anxiety, their medical provider may be more likely to prescribe a beta-blocker (Farzam, 2021).
Other types of anti-anxiety medications
There are a few other drugs that healthcare providers occasionally prescribe for the treatment of anxiety. These include:
Buspirone (Buspar), a mild tranquilizer sometimes used to treat generalized anxiety disorder. The effects are similar to those of benzodiazepines, but without the risk of dependence (Chand, 2021).
Antipsychotics, which are not FDA-approved for anxiety but are sometimes helpful for people with generalized anxiety disorder (Garakani, 2020).
Antihistamines, which may be safer than other drugs for kids, and can also help with insomnia (Garakani, 2020).
There are others. But the ones above are far and away the most common.
Do anxiety medications work?
For some people, yes. All of the types of medication mentioned above are backed by solid research. That said, not everyone with anxiety will respond to medication. In fact, about 1 in 3 people with anxiety don’t find durable relief in the form of a pill (Garakani, 2020).
For these people—and for many others with anxiety—the best treatment may involve other forms of therapy, including psychotherapy (Chand, 2021).
What exactly is anxiety?
Technically, it’s a mood state fueled by worry and fear. This worry or fear tends to be “future-oriented,” meaning it’s about something that may or may not happen—as opposed to something that is happening in the present.
But anxiety isn’t just a mood. It’s a complicated experience that also involves thoughts, feelings, and behaviors (Chand, 2021).
The common symptoms of anxiety can be broken down into three categories.
Cognitive symptoms
The first category involves cognitive symptoms. These include (Chand, 2021):
Worry
Fear of losing control
Fear of injury or death
Fear of “going crazy”
Fear of negative judgment from others
Poor concentration
A sense of unreality or detachment
Physical symptoms
The second category involves the body. These symptoms include (Chand 2021):
Racing heart
Shortness of breath
Sweating or sweaty palms
Muscle tension
Rapid breathing
Hot flashes
Nausea
Upset stomach
Weakness or unsteadiness
Behavioral symptoms
The final category includes behavioral symptoms. Some of these are (Chand, 2021):
Avoiding certain things or situations
Urge to escape or flee
Moving away from sources of fear or worry and toward safer situations
Seeking reassurance
The different types of anxiety
There are many different anxiety medications in part because there are many kinds of anxiety. All of them involve some form of fear or worry.
General anxiety disorder, for example, involves persistent, hard-to-control worry about any number of different concerns—school, work, family, etc. Meanwhile, social anxiety disorder involves a fear of being around other people who may cause you to feel judged, embarrassed, or otherwise uncomfortable (Chand, 2021).
If you feel like you may benefit from anxiety medication, your healthcare provider can help you figure out whether a drug can help—and which one is best for you.
DISCLAIMER
If you have any medical questions or concerns, please talk to your healthcare provider. The articles on Health Guide are underpinned by peer-reviewed research and information drawn from medical societies and governmental agencies. However, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Bandelow, B., Michaelis, S., & Wedekind, D. (2017). Treatment of anxiety disorders. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 19 (2), 93–107. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2017.19.2/bbandelow. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5573566/
Bystritsky, A. (2021). Pharmacotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder in adults. In: UpToDate . Retrieved from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacotherapy-for-generalized-anxiety-disorder-in-adults#H303453001
Chand, S. P., & Marwaha, R. (2021). Anxiety. In StatPearls . Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470361/
Chu, A., & Wadhwa, R. (2021). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. In StatPearls . Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554406/
Farzam, K., & Jan, A. (2021). Beta Blockers. In StatPearls . Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532906/
Garakani, A., Murrough, J. W., Freire, R. C., Thom, R. P., Larkin, K., Buono, F. D., & Iosifescu, D. V. (2020). Pharmacotherapy of anxiety disorders: current and emerging treatment options. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11 , 595584. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.595584. Retrieved from https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.595584/full
Gillman P. K. (2007). Tricyclic antidepressant pharmacology and therapeutic drug interactions updated. British Journal of Pharmacology, 151 (6), 737–748. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707253. Retrieved from https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707253
National Health Services (NHS). (2018) Overview: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). National Health Service (UK) . Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/talking-therapies-medicine-treatments/medicines-and-psychiatry/ssri-antidepressants/overview/
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). (n.d.). Any anxiety disorder. Retrieved June 1, 2021 from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/any-anxiety-disorder
Rickels, K., Etemad, B., Khalid-Khan, S., Lohoff, F. W., Rynn, M. A., & Gallop, R. J. (2010). Time to relapse after 6 and 12 months' treatment of generalized anxiety disorder with venlafaxine extended release. Archives of General Psychiatry, 67 (12), doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.170. Retrieved from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21135327/
Santarsieri, D., & Schwartz, T. L. (2015). Antidepressant efficacy and side-effect burden: a quick guide for clinicians. Drugs in Context, 4 , 212290. doi: 10.7573/dic.212290. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4630974/
Sheffler, Z. M., & Abdijadid, S. (2021). Antidepressants. In StatPearls . Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538182/
Taylor, M. J., Freemantle, N., Geddes, J. R., & Bhagwagar, Z. (2006). Early onset of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant action: systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63 (11), 1217–1223. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.11.1217. Retrieved from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17088502/
Vashchinkina, E., Panhelainen, A., Aitta-Aho, T., & Korpi, E. R. (2014). GABAA receptor drugs and neuronal plasticity in reward and aversion: focus on the ventral tegmental area. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 5 , 256. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00256. Retrieved from https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2014.00256/full










